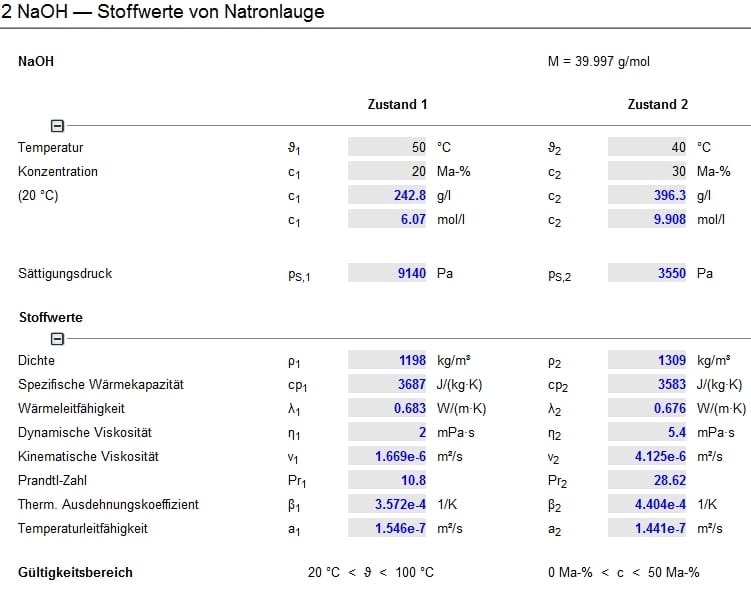
Sodium Hydroxide Specific Heat Capacity
A modified commercial (Setaram C80) calorimeter has been used to measure the isobaric volumetric heat capacities of concentrated alkaline sodium aluminate solutions at ionic strengths from 1 to 6 mol kg −1, with up to 40 mol.% substitution of hydroxide by aluminate, at temperatures from 50 to 300 °C and a pressure of 10 MPa. Jun 22, 2019 If water has a specific heat capacity of 4200 J/(Kg.degK), the specific heat capacity will range from 4200 to 1491.5 J/(Kg.degK) as you increase the mass fraction of NaOH in your solution from 0% to 100%. Sodium hydroxide, also known as lye and caustic soda, 1 2 is an inorganic compound with the formula. Temperature (K) 298. A: 419.4837: 86.02304: B-1717.754: 0.000000: C: 2953.573: 0.000000: D-1597.221: 0.000000: E-6.046884: 0.000000: F-517.8662-448. The DOW reference is good because they make Sodium Hydroxide. A good library reference on chemicals is Perry's Handbook of Chemical Engineering. It has a table of Sodium Hydroxide heat capacities for solutions. And NO, the density of a solution is NOT the same as water unless it is very dilute. Swampie777 ( Chemical Engineer).

Click to see full answer.
Similarly, what is the heat of neutralization of HCl and NaOH?
The heat of reaction of one mole of H+ and OH- is 57.3 KJ. So, the heat of neutralisation of HCl and NaOH will be very cery close to 57.3 KJ per mole( As Both HCl and NaOH are strong elctrolytes so both of them quite easily without any considerable expense of energy furnish H+ and OH- ions respectively.
why is the reaction between NaOH and HCl exothermic? - When a reaction is endothermic - Bonds are broken and energy is absorbed from the surroundings. In your example of HCl + NaOH - this is a neutralisation reaction to form NaCl + H20. Basically there is more bond making than bond breaking in this reaction so the Delta H is negative - it is more exothermic.
In this manner, what equation is appropriate to calculate the heat produced from the HCl NaOH reaction?

Calculate the number of moles of base you add to determine the molar heat of neutralization, expressed using the equation ΔH = Q ÷ n, where 'n' is the number of moles. For example, suppose you add 25 mL of 1.0 M NaOH to your HCl to produce a heat of neutralization of 447.78 Joules.
50% Sodium Hydroxide Specific Heat Capacity
Is the reaction between HCl and NaOH endothermic or exothermic?
Specific Heat Capacity Of Water
This reaction is classified as an exothermic reaction. The reaction of HCl(aq), a strong acid, with NaOH(aq), a strong base, is an exothermic reaction.